Every student who studies math has this big question in his/her mind ; what is ln? Let me briefly answer this question. “ln” is a special type of logarithm which is called natural logartihm.This logartihm has the base number “e” (we are going to explain what is the number “e” is ,and where it is used?”)
Big Question ; “What is ln?”
Every student who studies math has this big question in his/her mind ; what is ln?
Let me briefly answer this question.
In mathematics, the natural logarithm, denoted by ln, is a function that is used to represent the inverse of the exponential function. The natural logarithm has several important properties and applications in mathematics and science, and it is an essential tool for solving a wide range of problems involving exponential growth and decay.
One of the most important properties of the natural logarithm is that it allows us to convert exponential equations into linear equations, which are much easier to solve. For example, if we have an equation of the form y = b^x, where b is the base of the exponent and x is the exponent, we can take the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation to get ln y = xln b. This equation is now in linear form, and we can use standard techniques to solve for x.
Another important property of the natural logarithm is that it allows us to compare the relative growth or decay of two exponential functions. For example, if we have two functions of the form y = a^x and z = b^x, we can take the natural logarithm of both functions to get ln y = xln a and ln z = xln b. By comparing the values of ln a and ln b, we can determine which function is growing or decaying more rapidly.
In addition to its mathematical properties, the natural logarithm has numerous applications in science and engineering. It is used to model exponential growth and decay in a variety of fields, including biology, economics, and physics. It is also an essential tool for solving problems involving compound interest, radioactive decay, and population growth.
Overall, the natural logarithm is a powerful and versatile function that is essential for understanding and analyzing exponential growth and decay. Its properties and applications make it an important tool for solving a wide range of problems in mathematics and science.
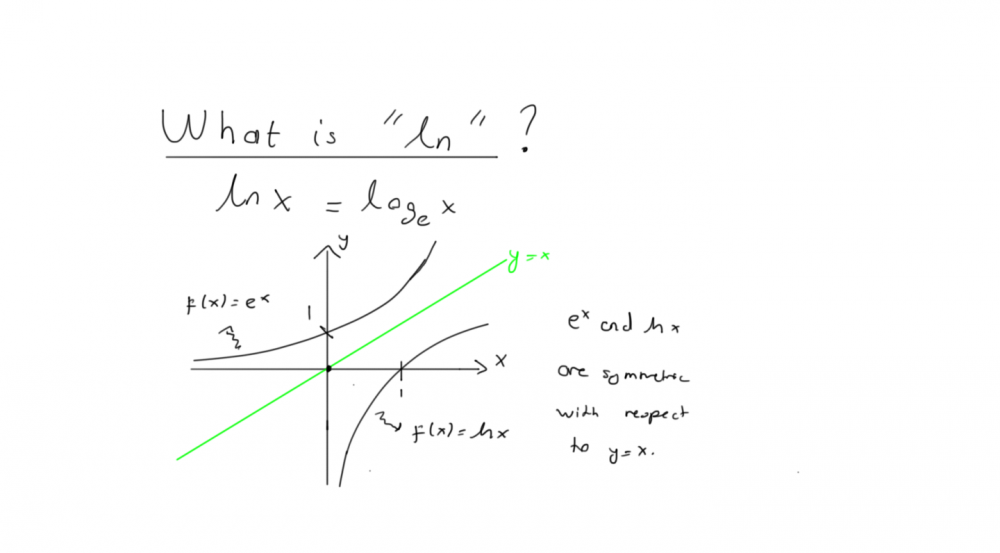
“ln” is a special type of logarithm which is called natural logartihm.This logartihm has the base number “e” (we are going to explain what is the number “e” is ,and where it is used?”)
log=logarithm ln=logarithm natural
ln(x)=logex
It is the inverse of y=ex function.
So you shouldn’t be hesitated when you see “ln”.Don't forget that it is a logarithm function and all of the logarithm rules can be used for “ln”.
Let’s look at the some rules of natural logarithm
lne=1
ln(x.y)=lnx+lny
ln(x/y)=lnx – lny
ln( ax )=a*ln(x)
ln(1/x)=-ln(x)
And derivative of the function of y=ln(x) is dy/dx=1/x
Also antiderivative of the function y=1/x is y=ln(x) ( ∫1/x dx=ln(x))
And if you need to study for more logarithms,logarithmic functions you can visit our questionbank.
Please click here.